The Centers for Advanced Orthopaedics is redefining the way musculoskeletal care is delivered across the region with locations throughout Maryland, DC, Virginia and Pennsylvania.
Stress Fractures: Causes, Risks, and Treatment
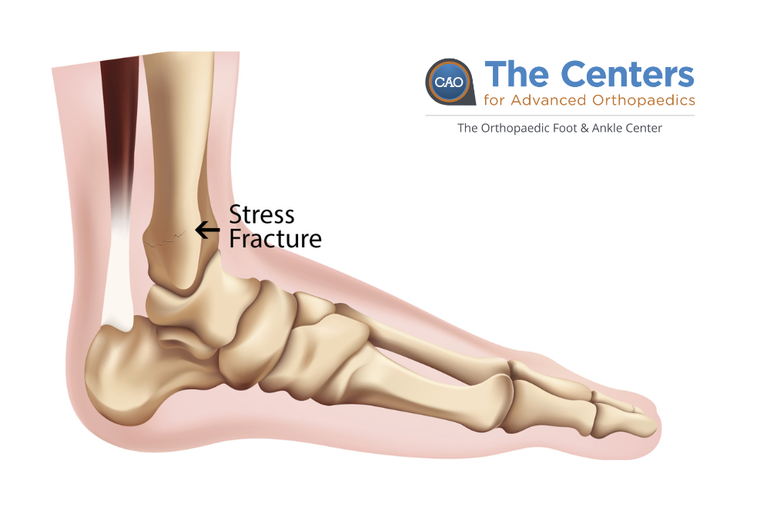
Stress fractures are a common type of overuse injury, often seen in athletes and active individuals. These tiny cracks in the bones occur when muscles become fatigued and can no longer absorb the impact from repetitive activity. When muscles are overworked, they transfer the stress to the bones, causing small cracks or fractures. Stress fractures typically occur in the weight-bearing bones of the foot and lower leg, with the second or third metatarsals (the long bones between the toes and the midfoot) being the most commonly affected. Other common locations include the heel, the fibula (outer bone of the lower leg), and the navicular bone on the top of the midfoot.
Who's at Risk?
Certain groups are more likely to develop stress fractures, including:
- Athletes in high-impact sports such as runners
- Adolescents with immature bones that are still developing
- Female athletes with abnormal menstrual cycles, leading to decreased bone mass
- Military recruits undergoing intense physical training
- Adults with osteoporosis or weakened bone structure
Causes of Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are often caused by repetitive stress on the bones. Contributing factors include:
- Doing too much too soon during training or physical activity
- Using improper sports equipment
- Wearing shoes that are too worn or stiff
- Changing the surface on which you exercise (e.g., moving from grass to pavement)
- Training or technique errors
- Foot deformities such as flat feet or bunions
Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to recognize the early signs of a stress fracture to prevent further damage. Common symptoms include:
- Gradual pain that worsens with weight-bearing activities and subsides with rest
- Swelling on the top of the foot or outside the ankle
- Tenderness to the touch at the fracture site
- Possible bruising in the affected area
Diagnosing a Stress Fracture
If you suspect a stress fracture in your foot or ankle, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Stop the activity and rest the injured foot to avoid worsening the condition. Apply an ice pack and elevate the foot above heart level to reduce swelling. Refrain from putting weight on the foot until you can see a doctor.
Ignoring the pain could lead to a complete break in the bone, resulting in a longer recovery process.
Treating Stress Fractures
Treatment will depend on the location of the stress fracture. Most stress fractures will heal if you reduce your level of activity and wear protective footwear for two to four weeks. Your orthopaedist may recommend that you wear a stiff-soled shoe. Athletes should switch to a low-impact sport such as swimming or bicycle riding. Your doctor may apply a cast or boot to your foot or recommend that you use crutches until the bone heals. Stress fractures that don’t heal properly can develop into breaks in the bones. In some cases, you may need surgery to ensure proper healing.
At The Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Center, we provide comprehensive care for stress fractures and other foot and ankle injuries. If you’re experiencing symptoms or have concerns, our team is here to help you get back on your feet.